Hybrid Energy Storage Systems
This project proposes the use of a bi-directional DC/DC power electronic circuitry for the hybrid energy storage system (HESS) to drive an electric vehicle motor.
The proposed HESS is composed of a battery storage unit and an ultra-capacitor (UC). Batteries and UCs are both energy storage devices but with different features. The high energy density of the batteries is suitable for constant speed driving intervals while the high power density of the UCs is applicable for intermittent driving operations. Figure 1 shows the different characteristics of the two devices.
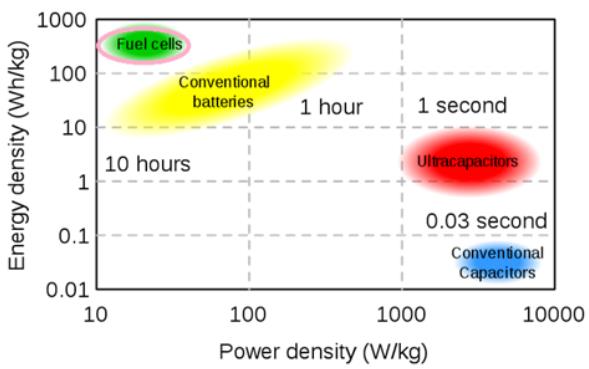
Figure 1. Power and Energy Density for Different Storage Devices
As a result, the optimum DC-bus voltage is easily regulated in both the generating and the motoring regions of the electric machine.
Figure 2 shows a general schematic for the proposed HESS configuration along with
the control structure.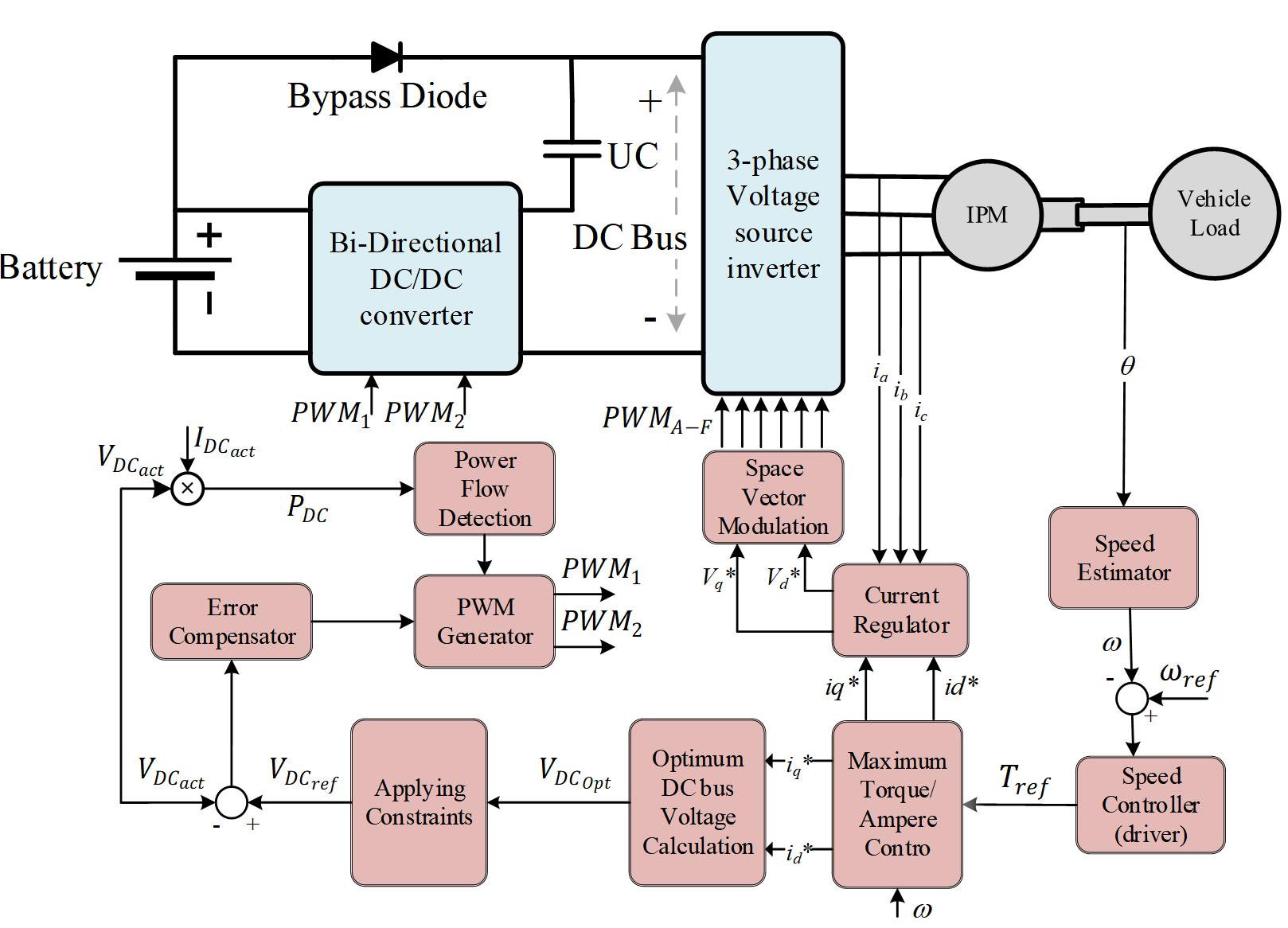
Figure 2. The proposed HESS Configuration and Control Structure
This work had been technically accepted through a peer review process that resulted in IEEE transaction publications and conference presentations.
However, the next step in this project is to build the system for high power ratings, test and evaluate its performance and cost compared to the conventional battery based electric vehicles.
The steps need to be taken for this project are:
- Storage devices sizing and selection.
- Power Electronic Architecture Design.
- DC/DC converter and DC/AC inverter design.
- Motor selection and testing.
- Implementation of a coordinated control system.
- Testing the system and evaluating the results relative to the conventional designs.